Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced financial markets, speed and accuracy are of the utmost importance. This is where algo trading (short for algorithmic trading) steps in, revolutionizing how trading is performed. But what is algo trading? Let’s break down this innovative method of trading and investing, its benefits, risks, and why it is reshaping the trading landscape.
Table of Contents
What is Algo Trading?
Algo trading has grown exponentially in recent decades, accounting for a growing portion of trading volume in global markets. Many investors, traders, and beginners ask: What is algo trading? Algo trading is using computer programs and mathematical models to automate buying and selling decisions in financial markets. These algorithms analyse vast amounts of data, such as price trends, volume, time, and even news sentiment, to execute trades at the best moment. Unlike manual trading, which relies on human judgment and is influenced by human emotions, what makes algo trading unique is its ability to process and act on data in milliseconds.
The term “algo trading” encompasses strategies ranging from simple (for example, “buy when the 50-Day Moving Average (DMA) crosses above the 200-DMA”) to complex machine-learning-driven systems. For instance, an algorithm buys 100 shares of company X whenever its 75 DMA crosses above the 200 DMA, executing the trade immediately without human intervention. This automated process eliminates the need to constantly monitor price charts and enables precise, emotion-free execution.
How Algo Trading Works?
For more clarification, let’s ask again: What is algo trading? The answer lies in combining computer science with the financial market. First, a strategy is defined mathematically or logically (for example, “Buy Stock X if its price is above ₹ 50”). Next, this strategy is coded in software connected to a trading exchange or brokerage platform. Then, when deployed, the algorithm continuously monitors market data such as price, volume, news, market sentiment, etc., in real time, checking its programmed conditions. If the given conditions are met, the algorithm immediately sends the order to the exchange (namely, NSE and BSE) and executes the trade.
Traders often backtest algorithms using historical market data to monitor the applicability of rules. Once live, an algorithmic system can execute thousands of trades in a short period of time if conditions are right. This scale and speed allow traders to operate in multiple markets (stocks, forex, commodities, cryptos, currencies, etc.) all the time without having to sit at a terminal. For example, an algo can split a large order into many smaller ones (iceberg orders), hiding market effects and improving execution. Technologies such as low-latency networks and placing trading servers close to the exchange’s servers (co-location) further reduce the time between trading decisions and execution.
Common Algo Trading Strategies:
The algo trading encompasses a wide range of strategies. Some common strategies are as follows:
Trend Following:
This strategy identifies and follows the market trend. For example, an algorithm might buy the stocks that are rising in price, analysing the technical indicators, and sell those that are falling.
Market Making:
Algorithms capture the bid-ask spread through placing buy and sell limit orders on both sides of the order book. Market-making bots aim to profit from the difference between the buy and sell prices. It provides liquidity to the market.
Arbitrage:
The algorithm looks for differences in the prices of the same asset in different markets or assets, buying it at a lower price in one market and selling it at a higher price in the other market. If a stock is trading slightly cheaper on one exchange and higher on another, an arbitrage bot will immediately buy at a lower price and sell at a higher price, making a small profit before the gap closes. Let’s say a stock of company X is priced at ₹ 50.50 on the NSE and ₹ 50.60 on the BSE. The bot will then buy it at ₹ 50.50 on the NSE and sell it at ₹ 50.60 on the BSE, making a profit of 10 paise on each stock.
Statistical (Mean-Reversal) Trading:
These models bet that prices will eventually return to a historical average. For example, if the stock price of Company Y deviates significantly from its average level, the algorithm may trade in anticipation of a reversal.
VWAP/TWAP Execution:
Volume- or time-based average pricing strategies break up large orders into smaller orders, which are executed evenly throughout the day (TWAP) or proportionally to market volume (VWAP). This helps large investors get the average price without moving the market too much.
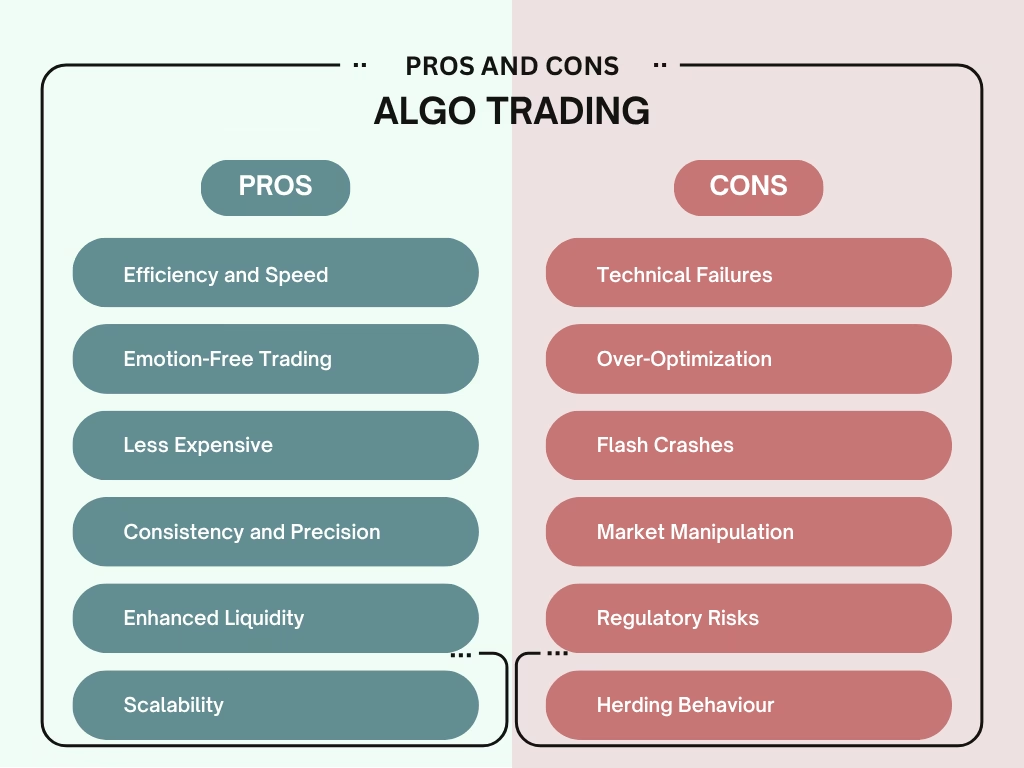
Benefits of Algo Trading:
Algo trading offers several benefits to institutional as well as retail traders, which is why it is popular among them. Some of the key benefits are as follows:
Efficiency and Speed:
Computers capture opportunities in milliseconds because they execute orders much faster than humans, allowing traders to respond instantly to market changes and news.
Emotion-Free Trading:
Algorithms adhere strictly to their instructions, steering clear of emotional decision-making or panic-selling. As a result, trades are grounded entirely in data and strategy, rather than fear or greed.
Less Expensive:
Algo trading can lower the transaction costs and fees by cutting out large orders. By breaking large trades into smaller ones, algorithms can achieve lower average prices and reduce market impacts.
Consistency and Precision:
Algos stick to the plan (e.g., buy at ₹ 50 means that the algo will buy at ₹ 50, not higher or lower) without any errors or mistakes. Before deployment, strategies can be backtested to further improve performance based on historical data.
Enhanced Liquidity:
Algos continuously place and cancel orders; in this way, they help to tighten the bid-ask spread, which benefits the entire market by enhancing liquidity.
Scalability:
A single algorithm can simultaneously monitor and trade multiple securities or markets, something no human trader can realistically do. This broad range allows opportunities to be exploited across asset classes (stocks, bonds, futures, cryptos, currencies, etc.) in parallel.
Risks and Challenges:
Along with its benefits, algo trading also carries some risks, which are as follows:
Technical Failures:
Algorithms are unable to function on their own, so they rely on software, hardware, and data feeds. Trades can be incorrect due to errors in the code, frozen screens, or connectivity issues. Historical errors (such as fat finger errors or feed interruptions) have caused unintended large losses or erratic trading behaviour.
Over-Optimization:
Subtly changing the algorithm based on past data can have the opposite effect on the live market. A strategy that is “curve-fitted” to the historical pattern may act poorly in the new market conditions.
Flash Crashes:
Automated systems can operate simultaneously and rapidly, causing sudden changes in the market. For example, in 2010, algorithmic selling by high-frequency traders triggered a “flash crash” that wiped out nearly $1 trillion in equity value in a matter of minutes.
Market Manipulation:
Some algorithms may be misused to manipulate the market by sending fake orders (spoofing) or creating a false impression of demand. To avoid these misuses, regulators continuously monitor the market, but monitoring the nanosecond trades is challenging.
Regulatory Risks:
Some financial institutions require algo traders to test and register their systems under different rules. Firms must constantly keep up with evolving regulations, reporting requirements, and compliance procedures.
Herding Behaviour:
When many firms use similar models and signals, the price may move in a specific direction. During the period of stress, firms may simultaneously sell or buy, leading to some significant price movement. This phenomenon, called the herding effect, is increasingly concerning as more traders adopt similar algorithmic systems.

Impact on Market:
The way markets operate globally has dramatically changed thanks to algo trading. Today, it accounts for a large portion of trading volume in stocks, forex, options, and other asset classes. For example, in India, approximately 50-55% of traders use algorithms for trading, whereas in the USA, Europe, and other Asian markets, the number rises to about 60-70% of the total trading volume.
This development has both advantages and disadvantages for investors. On the positive side, algorithms can post orders 24/7 and respond to news immediately, resulting in more liquid markets and tighter spreads, and investors often see reduced execution delays and better prices. However, on the negative side, markets can move more quickly, and anonymous algorithms can make it difficult to interpret price changes.
Future of Algo Trading:
Increased Use of AI and ML:
The future of algo trading depends on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Algorithms are becoming smarter through ML, which is helping them adapt to new market conditions without having to be reprogrammed. These AI-powered models can identify patterns that traditional strategies might miss.
Widespread Adoption Among Retail Traders:
Algo trading, previously limited to large institutions, is now becoming more accessible to retail traders. Thanks to low-code platforms, APIs, and broker-provided tools, even individual investors can now create and test automated strategies.
The Rise of Alternative Data:
Retail traders are now enriching their algorithms with non-traditional data sources such as social media sentiment and news feeds, giving them a head start over their competitors.
Real-Time Risk Management:
Risk management plays a crucial role in any type of trading. Future algorithms will include built-in risk monitoring tools that will dynamically adapt to volatility and news, thereby reducing the risk of flash crashes and unexpected market changes, providing a safe automated trading experience.
Tighter Rules and Regulations:
As algo trading gains popularity, regulators are introducing more regulations to ensure fairness and transparency. Tighter rules on testing, reporting, and ethical use of AI should be introduced to keep markets stable and reduce manipulative practices like spoofing.
Integration With Crypto Market:
Algorithmic trading is gaining traction in cryptocurrency markets, which run 24/7. Future systems will likely integrate blockchain data and decentralized finance indicators to trade digital assets more efficiently.
Conclusion:
As financial markets become increasingly complex and fast-paced, algo trading has emerged as a powerful tool to navigate this market with precision and speed. By now, the question “What is algo trading?” should be clearer; it is to use computer programs to execute trades based on predetermined rules, eliminating human emotion and increasing efficiency.
Algo trading is no longer just for large institutions, as technology advances, retail investors and traders are also exploring automated strategies. While its benefits are significant, such as speed, accuracy, and scalability, it is equally important to understand the associated risks, such as technical errors, model overfitting, market manipulation, or regulatory challenges.
Ultimately, it can be said that the future of algo trading looks promising, driven by AI, alternative data, and real-time analytics. By reading this article, investors or traders can understand the basics of algo trading and potentially gain a competitive edge in this digital era.